i.Mune® NEO [CE]

i.Mune NEO [CE] is a quantitative in vitro diagnostic test to determine the percentages of lymphocyte subsets in newborn capillary whole blood specimens collected and dried on filter paper.
i.Mune NEO [CE] is suitable for epigenetic quantification of:
- T lymphocytes (CD3+)
- T helper lymphocytes (CD3+CD4+)
- Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CD3+CD8+)
- Memory T helper lymphocytes (CD3+CD4+CD45RA+)
- B lymphocytes (CD19+)
- Natural killer cells (CD16+CD56dim) (NK)
in dried blood spot (DBS) samples from newborns
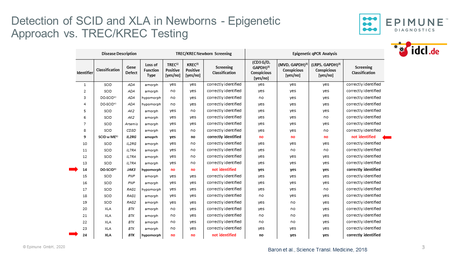
Proof of concept: Epigenetic immune cell quantification allows early detection of inborn errors of immunity in newborns.

A cohort of 250 apparently healthy newborns and 24 confirmed SCID and XLA cases was analyzed using epigenetic immune cell quantification of T-, B- and NK cells in dried blood spot samples2)
23 out of 24 confirmed SCID or XLA cases were correctly identified using the epigenetic immune cell quantification method.
Using combined TREC/KREC Analysis, 22 out of 24 cases were correctly identified2)
Epigenetic immune cell quantification identifies false-positive SCID screening cases (Blom et al., 2021)1)
Applications:
-
Early detection of immune cell dysregulation in newborns
- Confirmation of a conspicuous SCID screening result in newborns
**The above applications are currently tested in several studies
Literature
- Blom, M et al. Second Tier Testing to Reduce the Number of Non-actionable Secondary Findings and False-Positive Referrals in Newborn Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol (2021).
- Baron U et al., Epigenetic immune cell counting in human blood samples for immunodiagnostics. Sci Transl Med. 2018 Aug 1;10 (452)